

Description
x- Highly effective form of choline for brain health
Choline is a semi-essential nutrient whose Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) according to the Institute of Medicine is 425 mg/day for women and 550 mg/day for men. Many people are unable to obtain adequate amounts of choline through diet and endogenous synthesis (from phosphatidylethanolamine) is limited. Aging, genetic polymorphisms and estrogen deficiency are factors that can increase the body's demand for choline above the RDA.
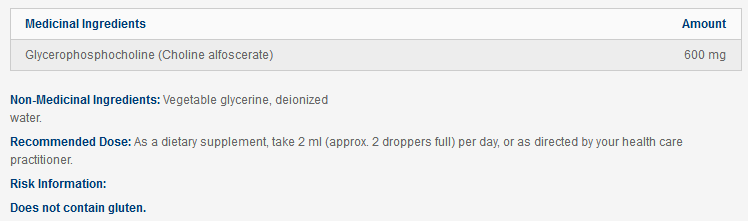
Glycerophosphocholine (GPC, also known as L-alpha-glycerylphosphorylcholine or choline alfoscerate) is a source of choline found in small amounts in various foods (including breast milk) as well as in all human cells. GPC is a water-soluble molecule and appears to be a more effective source of choline than choline or phosphatidylcholine (PC) from diet or supplementation.
GPC is well absorbed orally and is cleaved within enterocytes into glycerol-1-phosphate and choline. Following ingestion of GPC, plasma choline levels increase rapidly and can remain elevated for up to ten hours. A high plasma concentration of choline stimulates its transport across the blood-brain barrier very effectively. This increases choline stores inside neurons, where it will then be used for the synthesis of PC and acetylcholine.
Infos nutritionnelles
x- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.

